 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 1 of 40
19)
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Version
Effective Date
1
13 February 2020
1.1
18 June 2020
1.2
9 September 2020
1.3
25 March 2021
1.4
21 September 2021
1.5
18 February 2022
1.6
2 March 2022
1.7
5 March 2022
1.8
11 March 2022
1.9
21 March 2022
1.10
31 March 2022
1.11
1 April 2022
1.12
14 April 2022
Document Number
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
Author
HA Task Force on Clinical Management on
Infection (TFCM)
Custodian
Central Committee on Infectious Diseases and
Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Approved by
Central Committee on Infectious Diseases and
Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Approval Date
14 April 2022
Next Review Date
13 February 2023
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 2 of 40
19)
Table of Contents
Section
Page
1
Purpose ................................................................................................
3
2
Scope ...................................................................................................
3
3
Introduction ..........................................................................................
3
4
Surveillance and reporting criteria ...................................................
3
5
Clinical Management .........................................................................
3
6
Use of Specific anti-COVID-19 treatments ....................................
5
7
Release from Isolation .......................................................................
21
8
Follow-up arrangement .....................................................................
21
9
References ...........................................................................................................
22
Annex A Important Drug Interactions with Paxlovid
(nirmatrelvir/ritonavir)^……………………………………………...
25
Annex B Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for
Severe COVID-19…………………………………………………..
26
Annex C Information and Consent form for experimental treatment of
COVID-19……………………………………………………………
28
Annex D Fact sheet on the use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (PaxlovidTM)……..
32
Annex E Fact sheet on the use of molnupiravir……………………………..
36
Annex F Quick sheet on oral antiviral for COVID-19 treatment……………
39
Annex G Principles of prescription of Paxlovid (oral antiviral) for treatment
of early COVID-19 infection………………………………………...
40
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 3 of 40
19)
1. Purpose
1.1.
To provide guidance on clinical management of patients with Coronavirus
Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
2. Scope
2.1.
For all healthcare workers at Hospital Authority
3. Introduction
3.1.
A new strain of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) which has not been previously
identified in human, was reported in Wuhan, China in December 2019. It
belongs to a clade of betacoronavirus distinct from those associated with
human severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory
syndrome (MERS). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) causes acute
respiratory infection and pneumonia. Symptoms include fever, malaise, dry
cough, shortness of breath, anosmia and ageusia. Some patients may have
respiratory symptoms without fever and some patients may also have diarrhea.
People of older age or having underlying chronic disease are at a higher risk
of deterioration into serious condition.
4. Surveillance and reporting criteria
4.1.
Please report suspected cases fulfilling the reporting criteria of Coronavirus
Disease 2019 (COVID-19) to the Central Notification Office (CENO) of CHP
via fax (2477 2770), phone (2477 2772) or CENO On-line
(https://cdis.chp.gov.hk/CDIS_CENO_ONLINE/ceno.html). The case definition
is available on the above website of CENO On-line. Both reporting criteria and
case definition are subject to change upon availability of further
epidemiological, clinical and virological data.
5. Clinical Management
5.1.
Isolate the patient(s) in airborne infection isolation room (AIIR) with standard,
contact, droplet and airborne precautions
5.2.
Notify via NDORS/ eNID, and update the confirmed patient data when
necessary
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 4 of 40
19)
5.3.
Patient clinical severity
Category
Description
Satisfactory Progressing well and likely to be discharged soon
Stable
With mild influenza-like illness symptoms
Serious
Require oxygen supplement of 3 to 6 L/min
Critical
Require intubation, ECMO, in shock, high flow oxygen with
flow rate > 6 L/min
5.4.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis can be established by either Rapid Antigen Test (RAT) or
RT-PCR of SARS-CoV-2.
For RAT, please follow manufacturer’s instructions to perform the test
and interpret the result.
Specimens for RT-PCR of SARS-CoV-2
Lower respiratory tract (always preferred): sputum or tracheal
aspirate (TA) if intubated or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) (if
bronchoscopy)
OR
Upper respiratory tract: Nasopharyngeal Flocked swab (NPFS) or
Nasopharyngeal Aspirate (NPA) [Pooled with throat swab in viral
transport medium] or Deep throat saliva (DTS)
Stool: For patient fulfilling reporting criteria with diarrhea, stool can
be sent to PHLSB for RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 testing
Repeated testing may be necessary to exclude the diagnosis. Please
consult the clinical microbiologists or infectious disease physicians for
advice
If patient has any stool sample being tested positive for SARS-CoV-2
previously, contact precaution should be maintained until negative
result from stool has been obtained
Microbiological workup as appropriate, e.g.
Sputum, urine and blood culture
NPA +/- Tracheal aspirate for flu A/B and other respiratory viruses
NPA +/- Tracheal aspirate for atypical pneumonia PCR
Urine for legionella and pneumococcal antigen
Other investigations e.g. CBP with D/C, L/RFT, CaPO4, glucose, ESR,
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 5 of 40
19)
CRP, procalcitonin, CXR and ECG, etc.
5.5.
Monitor vital signs and organ functions, and recognize complication(s) early
5.6.
Liaise with ICU early for intensive care if anticipate clinical deterioration
5.7. Provide supportive treatments
Monitor for any concomitant bacterial infections and start empirical
antibiotics if necessary
β lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combination or 3rd generation
cephalosporin +/- macrolide/doxycycline can be considered
Oxygen
IV fluid (conservative fluid management for severe respiratory failure)
Hemodynamic support
High-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) may be considered in selected patients
with hypoxemic respiratory failure. These patients should be closed
monitored for clinical deterioration.
Mechanical ventilation with protective lung ventilation +/- consider
ECMO for refractory respiratory failure
Renal replacement therapy (renal failure)
Consider proton pump inhibitors (PPI) for stress ulcer prophylaxis for
prevention of GI bleeding per clinical judgment of ID physician/
Intensivist for moderate to severe cases
5.8.
Anticoagulation
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19, use pharmacological
prophylaxis, such as low molecular weight heparin (such as enoxaparin
40mg Q24H subcutaneous, according to local and international
standards, to prevent venous thromboembolism, when not
contraindicated. For those with contraindications, consider mechanical
prophylaxis (intermittent pneumatic compression devices)
6. Use of Specific anti-COVID-19 treatments
6.1.
Unlicensed treatment should be given under ethically-approved clinical trials
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 6 of 40
19)
as far as possible. In the absence of appropriate clinical trials, the following
treatment regimens may be considered early, particularly in patients having
following conditions with increased risk of severe disease
Diabetes mellitus
Obesity (body mass index [BMI of 30kg/m2 or higher])
Age ≥60 years (unless otherwise specified)
Immunocompromised state
Underlying chronic illnesses
Incomplete COVID-19 vaccination #
6.2.
The following table summarizes different available treatment regimens. These
regimens are determined based on evidence extrapolated from research
performed for other coronaviruses, expert opinion, non-randomized placebo
controlled trials, case series and limited randomized placebo controlled trials
on treatment of COVID19, as well as the availability of therapeutics in Hong
Kong. This serves as an interim guidance and will be updated according to the
availability of new evidence or drug availability.
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 7 of 40
19)
Proposed Therapeutic management of adults with COVID-19
based on disease severity
•
For patients who are at risk of progressing to severe COVID-19
and at early onset of disease (within 5 days):
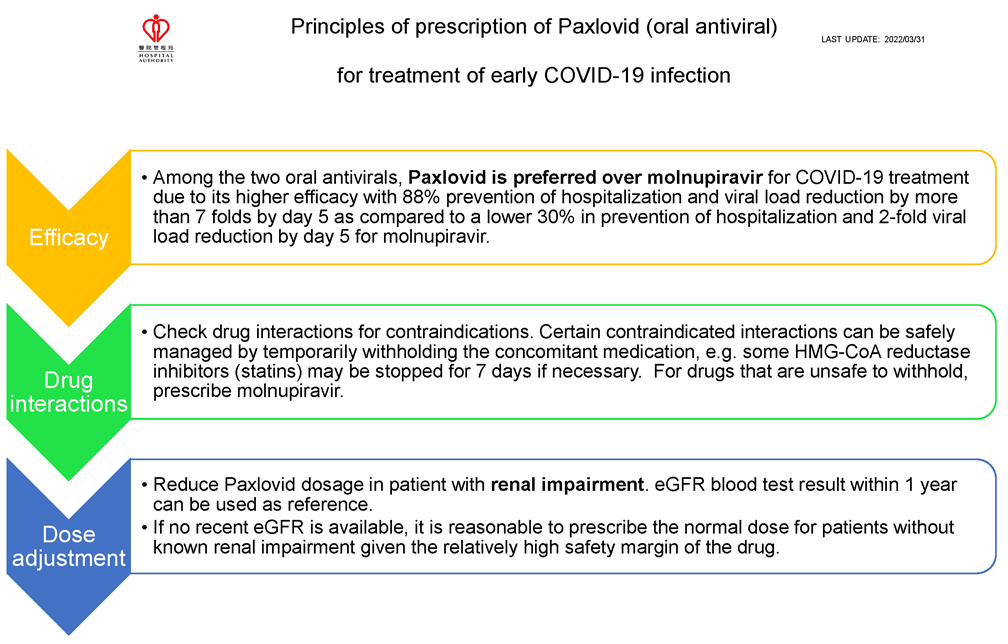
•Paxlovid (preferred if not contraindicated) or Molnupiravir
Mild symptoms, but •Amubarvimab/romlusevimab (within 10 days)
at risk of disease
•+/- can consider Interferon Beta-1b sc
progression
•
Use one of the following options:
Moderate
•Remdesivir (3-5 days) + dexamethasone; or
symptoms and
•Dexamethasone;
requiries
•+/- Interferon Beta-1b sc
supplemental
oxygen (SaO2 <94%
•
Use of remdesivir depending on the disease stage, guided by
RA)
symptom onset and CT value
•
Use one of the following options:
•Remdesivir (3-5 days) + dexamethasone; or
Moderate to severe •Dexamethasone;
symptoms and
requiring oxygen
•
Use of remdesivir depending on the disease stage, guided by
through a high-flow
symptom onset and CT value
device or NIV
•
For patients with rapidly increasing oxygen needs and systemic
inflammation, consider add either
baricitinib or
IV tocilizumab
to 1 of the 2 options above
•Dexamethasone
Critical disease
•
For patients who are within 24 hours of admission to ICU:
and requires
mechanical
•Dexamethasone + IV tocilizumab
ventilation or
ECMO
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 8 of 40
19)
6.3.
Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir)
Paxlovid is a combination of nirmatrelvir, a SARS-CoV-2 main protease
inhibitor that prevents viral replication, and ritonavir, an HIV-1 protease
inhibitor and CYP3A inhibitor that is not active against SARS-CoV-2 but
inhibits the metabolism of nirmatrelvir resulting in increased plasma
concentration of nirmatrelvir.
Dosage and administration: 300 mg nirmatrelvir (two 150 mg tablets)
with 100 mg ritonavir (one 100 mg tablet), with all three tablets taken
together twice daily for 5 days.
Pregnancy consideration: There are no available human data on the use
of nirmatrelvir during pregnancy to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of
major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Published observational studies on ritonavir use in pregnant women
have not identified an increase in the risk of major birth defects.
Published studies with ritonavir are insufficient to identify a drug-
associated risk of miscarriage. There are maternal and fetal risks
associated with untreated COVID-19 in pregnancy. The use of
nirmatrelvir and ritonavir should not be withheld from pregnant patients
when the potential benefits outweigh the possible risks (NIH 2022)
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: use of ritonavir may
reduce the efficacy of combined hormonal contraceptives. Advise
patients using combined hormonal contraceptives to use an effective
alternative contraceptive method or an additional barrier method of
contraception
Breastfeeding consideration: Ritonavir is present in breast milk;
excretion of nirmatrelvir is unknown. Lactation is not a contraindication
for use (ACOG 2022; FDA 2021). According to the manufacturer, the
decision to breastfeed during therapy should consider the risk of infant
exposure, the benefits of breastfeeding to the infant, and the benefits of
treatment to the mother (FDA 2021)
Warnings and precautions:
-
The concomitant use of Paxlovid and certain other drugs may
result in potentially significant drug interactions. Consult the ful
prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential
drug interactions. (Annex A)
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 9 of 40
19)
-
Allergic Reactions/Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions
have been reported with Paxlovid. If signs and symptoms of a
clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction or anaphylaxis occur,
immediately discontinue Paxlovid and initiate appropriate
medications and/or supportive care.
-
Hepatotoxicity: Hepatic transaminase elevations, clinical hepatitis,
and jaundice have occurred in patients receiving ritonavir.
-
HIV-1 Drug Resistance: Paxlovid use may lead to a risk of HIV-1
developing resistance to HIV protease inhibitors in individuals with
uncontrolled or undiagnosed HIV-1 infection
Adverse reactions
-
Dysgeusia, diarrhea, hypertension, and myalgia.
Renal impairment: dose reduction for moderate renal impairment (eGFR
≥30 to <60 mL/min): 150 mg nirmatrelvir (one 150 mg tablet) with 100
mg ritonavir (one 100 mg tablet), with both tablets taken together twice
daily for 5 days. Paxlovid is not recommended in patients with severe
renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min)
-
From operational perspectives, the most recent eGFR result within
1 year can be used as reference. For patients without recent eGFR
result available and without known renal impairment, it is
reasonable to prescribe normal dose given the relatively high
safety margin of the drug.
Hepatic impairment: Paxlovid is not recommend in patients with severe
hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C).
Paxlovid may be used in paediatric patients (12 years of age and older
weighing at least 40 kg). Please refer to paediatric guidelines for dosage.
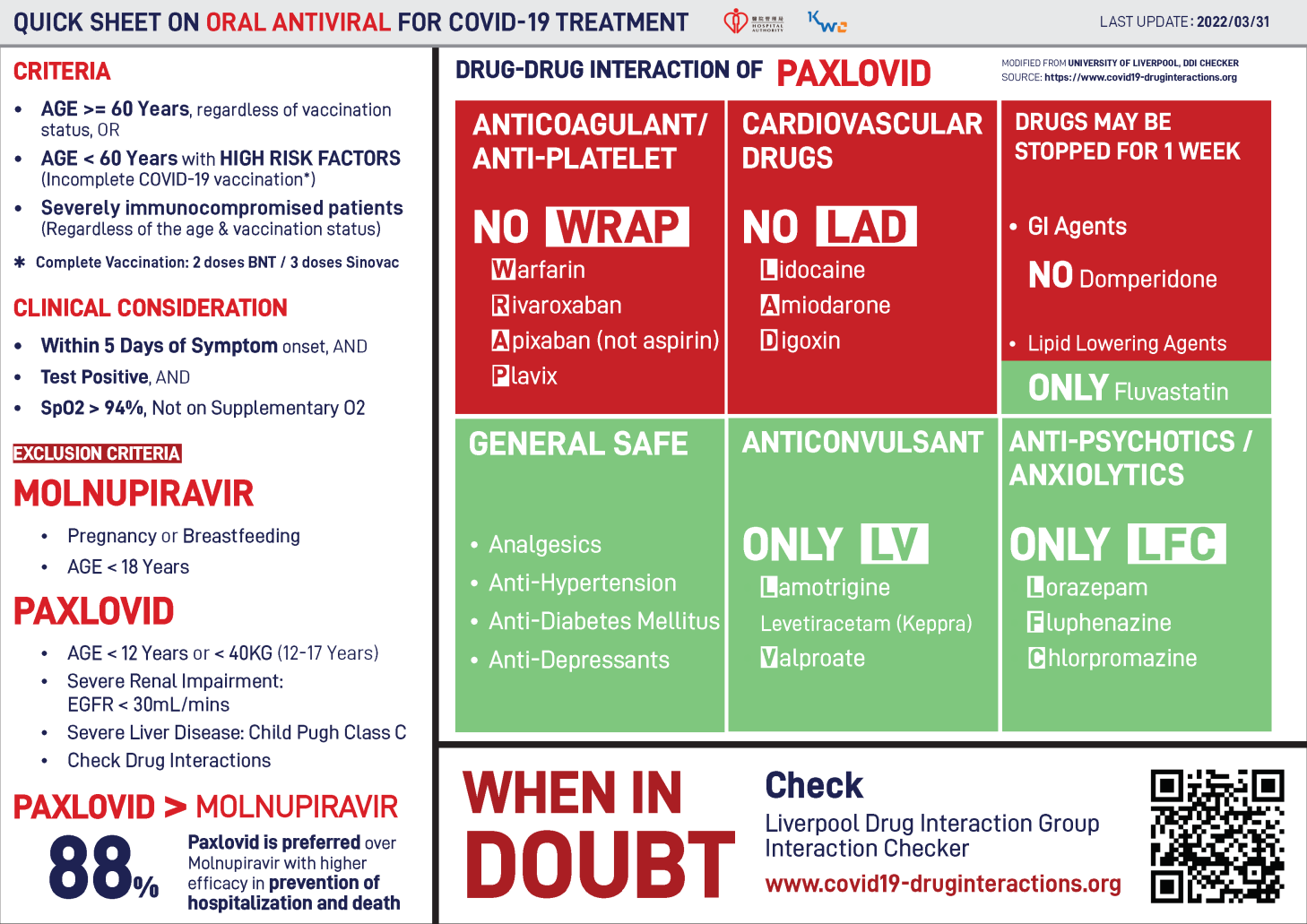
Criteria for use
Age ≥ 60 years (regardless of vaccination status), OR
Age < 60 years with high risk factors (Annex B) AND incomplete
vaccination #, OR
Severely immunocompromised individuals @ (regardless of
vaccination status)
Clinical consideration
Within 5 days of symptom onset, AND
Test positive (RAT/PCR), AND
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 10 of 40
19)
SpO2 > 94% (room air)
Exclusion criteria
Patients less than 12 years of age or weighing below 40 kg (for 12-17
years of age)
6.4. Molnupiravir
Molnupiravir is a nucleoside analogue that inhibits SARS-CoV-2
replication by viral mutagenesis.
Dosage and administration: 800 mg (four 200 mg capsules) taken orally
every 12 hours for 5 days, with or without food.
Pregnancy consideration: Based on findings from animal reproduction
studies, molnupiravir may cause fetal harm when administered to
pregnant individuals. The use of molnupiravir is NOT recommended
during pregnancy. Advise individuals of childbearing potential to use
effective contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, for the
duration of treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of molnupiravir.
For sexually active males with partners of childbearing potential, they are
advised to use a reliable method of contraception correctly and
consistently during treatment and for at least 3 months after the last dose
of molnupiravir (the risk beyond three months after the last dose of
molnupiravir is currently unknown).
Breastfeeding consideration: The use of molnupiravir is NOT
recommended for breastfeeding women.
Warnings and precautions:
Embryo-fetal toxicity
Hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, angioedema, erythema, rash, and
urticaria adverse reactions have been identified during post-
authorization use of molnupiravir.
Bone and cartilage toxicity: Molnupiravir should not be used in
patients less than 18 years of age because it may affect bone and
cartilage growth.
Adverse reactions
Diarrhea, dizziness, headache, skin itchiness, skin rash, nausea,
vomiting.
Laboratory abnormalities in chemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine, and
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 11 of 40
19)
lipase) and hematology (haemoglobin, platelets, and leukocytes)
Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment in patients with any degree of
renal impairment is recommended. The pharmacokinetics of
molnupiravir and its metabolite NHC has not been evaluated in patients
with eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m^2 or on dialysis.
Hepatic impairment: No dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic
impairment is recommended. The pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir and
its metabolite NHC has not been evaluated in patients with moderate
and severe hepatic impairment.
Molnupiravir has not been studied in paediatric patients.
Criteria for use
Age ≥ 60 years (regardless of vaccination status), OR
Age < 60 years with high risk factors (Annex B) AND incomplete
vaccination #, OR
Severely immunocompromised individuals @ (regardless of
vaccination status)
Clinical consideration
Within 5 days of symptom onset, AND
Test positive (RAT/PCR), AND
SpO2 > 94% (room air)
Exclusion criteria
Pregnancy
Breastfeeding
Patients less than 18 years of age
6.5.
Remdesivir
Remdesivir is an antiviral and inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase
which perturbs viral replication. Remdesivir is given intravenously, once
daily after an initial loading dose.
3-5-day course for moderate to severe cases
(i)
Eligibility criteria:
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 12 of 40
19)
- Hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
AND
- Adults, and adolescents >=12 years of age and >= 40kg
AND
- eGFR based on Cockcroft-Gault equation >= 30ml/min
AND
- ALT below 5 times the upper limit normal at baseline
With
- pneumonia and SaO2 <94% on room air requiring
supplemental oxygen
AND
- Clinical deterioration with impending respiratory failure
- DTS or NPS+TS or sputum RT-PCR CTv <25
(ii)
Dosage: 200mg IV loading dose following by 100mg IV daily as
maintenance. The total duration of treatment should be 3-5 days
(iii)
Remdesivir should be sensibly used in cases with better
recovery potential and quality of life after recovery, in view of
limited drug supply
(iv)
Pregnancy: Remdesivir should be avoided in pregnancy unless
clinicians believe the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks to
the individual
(v)
Obtain consent for treatment. Major side effects: Phlebitis,
Nausea,
vomiting,
ALT
elevations,
hyperglycemia,
hyperbilirubinemia, hypersensitivity reactions, bradycardia
(vi)
Coadministration of remdesivir and interferon beta-1b may be
considered in the discretion of ID physicians, particularly in
severe patients with early onset of disease
(vii)
Stopping criteria:
Remdesivir should be discontinued in patients who develop any
of the following:
-
ALT >= 5 times ULN during treatment with remdesivir
-
ALT elevation accompanied by signs and symptoms of liver
inflammation or increasing conjugated bilirubin, alkaline
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 13 of 40
19)
phosphates, or INR
(viii) For patients with eGFR< 30ml/min: the benefit of using
remdesivir may outweigh the risk in selected patients. In such
scenario, the use of remdesivir is left to the discretion of
Infectious Diseases Physician in charge.
(ix)
Remdesivir is considered if meeting the above criteria and if
available. Some data suggest remdesivir may reduce time to
recovery and risk of mechanical ventilation. IDSA and the NIH
recommend remdesivir but WHO conditionally recommend
against remdesivir because a definitive mortality benefit has not
been shown.
6.6.
Interferon-based regimen
May consider the following regimen in confirmed patients who are at risk
of disease progression
Interferon beta-1b 0.25mg (8-16 MIU) subcutaneous daily*
(3 doses)
Pre-treatment workup
-
Check blood x CBP, LRFT, RG, LDH, CK, HBsAg, anti-HCV,
-
+ blood x TFT, ANA (for starting interferon)
-
CXR
-
ECG (if preexisting cardiac abnormalities or disease or clinically
indicated). For patients with underlying pre-existing cardiac
problems, follow-up monitoring of the cardiac condition is
suggested.
-
Pregnancy test for females with reproductive potential (Before
starting interferon or molnupiravir)
-
Avoid pregnancy in female patients and female partners of male
patients during and after molnupiravir therapy
-
Check any drug interactions with concomitant medications (in
particular, with ritonavir)
-
Obtain consent for treatment
(i)
Unlicensed indication and treatment is experimental
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 14 of 40
19)
(ii)
Side effects of treatment
(iii)
Contraindications:
Interferon beta-1b: history of hypersensitivity to
interferon beta, albumin; decompensated liver
disease, current severe depression and/or suicidal
ideation
Molnupiravir: pregnancy, breastfeeding
(iv)
For pregnant women, detailed explanation on the benefits
and potential risks should be provided before the
commencement of interferon beta-1b
(v)
For mentally incapacitated patients, may communicate
with next of kin and attain consent from them with proper
documentation.
*Dosing and frequency of interferon beta 1b can be adjusted at the
discretion of the Infectious Diseases Physician in charge
6.7.
Amubarvimab/romlusevimab (BRII-196/198)
Amubarvimab/romlusevimab is a human immunoglobulin G-1 (IgG1-λ)
monoclonal antibody cocktail that target the RBD of Spike protein of
SARS-CoV-2 with neutralizing action.
Dosage and administration
-
For adults and adolescents (12-17 years old, body weight ≥40kg)
dose of amubarvimab/romlusevimab is 1000mg respectively.
-
Each must be diluted with 100ml normal saline, before infusion by
intravenous route, at a rate of not more than 4ml/min
-
Administer amubarvimab first, followed immediately by
romlusevimab. In case romlusevimab is given first, amubarvimab
can be immediately given afterwards.
Pregnancy consideration
-
There are no available human data on the use of this drug during
pregnancy to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth
defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Amubarvimab/romlusevimab should be used only when clinicians
believe the benefits of treatment outweighs the risk to the individual
Breastfeeding consideration
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 15 of 40
19)
-
No data on presence or excretion of amubarvimab/romlusevimab
in human or animal breast milk. According to manufacturer, the
decision to breastfeed during therapy should consider the risk of
infant exposure, the benefits of breastfeeding to the infant, and the
benefits of treatment to the mother.
Contraindication
-
History of clinically significant hypersensitivity reactions to the
active ingredients (amubarvimab/romlusevimab) or any other
components
Warnings and Precautions
-
For the target group of adolescents at 12-17 years of age and body
weight ≥40kg, the approval of use is conditional as no clinical data
on efficacy and safety is available for confirmation at this stage
-
Allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with
amubarvimab/romlusevimab. If signs and symptoms of a
clinically
significant
hypersensitivity
reaction
or
anaphylaxis
occur,
immediately
discontinue
amubarvimab/romlusevimab and initiate appropriate
medical and/or supportive care.
-
Infusion-related reactions
During infusion and within 24 hours post-infusion,
observe for infusion-related reactions that may be severe
or potentially life-threatening, including:
-
Pyrexia, dyspnea, desaturation, chills, fatigue,
arrhythmia, chest pain, change in mental status,
nausea, headache, bronchospasm, hypotension,
hypertension, vasogenic edema, rash, pruritis,
myalgia, vasovagal reactions, dizziness, profuse
sweating.
If infusion-related reactions occur, consider slowing down
or stop the infusion, and initiate appropriate medical
and/or supportive care.
-
There have been reports of post monoclonal antibody treatment of
COVID-19 clinical deterioration, including fever, desaturation,
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 16 of 40
19)
dyspnea, arrhythmia, malaise, change in mental status, etc. Some
of them have led to hospitalization for treatment. It is not known if
these events are related to the use of monoclonal antibody or due
to natural progression of COVID-19 infection.
Adverse reactions
-
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurring in ≥1% of
participants in the ACTIV-2 Study through day 28 include:
Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, pyrexia, chills,
COVID-19 pneumonia, bronchitis, infusion-related
reactions, blood pressure increase, myalgia, headache,
insomnia, oropharyngeal pain, cough, dyspnea,
rhinorrhea and hypertension.
Renal impairment:
-
The effect of renal impairment on amubarvimab/romlusevimab
pharmacokinetics is still unknown
Hepatic impairment
-
The effect of hepatic impairment on amubarvimab/romlusevimab
pharmacokinetics is still unknown
Paediatric patients
-
Amubarvimab/romlusevimab is not yet approved for <12 years of
age or body weight <40kg. Amubarvimab/romlusevimab is
conditionally approved for adolescents of 12-17 years of age and
body weight ≥40kg without clinical trial data. Safety and efficacy in
paediatric patients have not been evaluated yet.
Geriatric patients
-
It
is
not
known
if
the
pharmacokinetics
of
amubarvimab/romlusevimab differ between geriatric and younger
adult patients.
Drug-drug interaction is unlikely given that amubarvimab/romlusevimab
is not expected to be renally excreted nor metabolized by the
Cytochrome P450 system
Criteria for use
-
The use of amubarvimab/romlusevimab can be considered in
patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection (by RAT or PCR) at
mild to moderate severity with risk factors for progression to severe
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 17 of 40
19)
disease and within 10 days of symptom onset.
-
The risk factors for progression to severe disease include the
following medical conditions according to manufacturer:
Age ≥60
Smoker
Immunosuppressed
Cirrhosis
Cancer
Obesity (defined as BMI>30kg/m2 for adults)
Pregnancy
Chronic kidney disease
Diabetes mellitus
Cardiovascular disease or hypertension
Chronic lung disease
Sickle cell disease
Neurodevelopmental disorder, inherited metabolic diseases
Patients on medical support e.g. tracheostomy, positive
pressure ventilation unrelated to COVID-19
Other illnesses or conditions on an individual risk-benefit
assessment basis
-
Monoclonal antibody should be used at the discretion of ID
physicians.
6.8.
Corticosteroids
Consider dexamethasone 6mg daily PO/IV up to 10 days in patients
with pneumonia, and requiring oxygen supplement or invasive
mechanical ventilation, Prolonged duration or higher dose of
dexamethasone may be considered according to individual clinical
condition
Equivalent total daily doses of alternative glucocorticoids are
methylprednisolone 32mg and prednisolone 40mg
Dexamethasone may cause hyperglycemia, viral rebound of SARS-
CoV-2 and increased risk of bacterial, fungal and parasitic infections
Use of short-period, stress dose steroids (hydrocortisone 200mg max
daily) for refractory septic shock or other clinical indications on
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 18 of 40
19)
physician discretion
6.9. Tocilizumab
Monoclonal antibody to IL6 receptor
There are data from clinical trials suggesting use of tocilizumab in
combination with dexamethasone in certain hospitalized patients who
are exhibiting rapid respiratory decompensation due to COVID-19,
including:
-
Recently hospitalized patients (i.e. within first 3 days of admission)
who have been admitted to intensive care unit (ICU) within the
prior 24 hours and who require invasive mechanical ventilation,
noninvasive ventilation, or high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC)
oxygen (>0.4 FiO2/ 30L/min of oxygen flow) or
-
Recently hospitalized patients (i.e. within first 3 days of admission)
not admitted to the ICU who have rapidly increasing oxygen
needs and require noninvasive ventilation or HFNC oxygen and
who have significantly increased markers of inflammation (CRP
>=75mg/L)
Dose: 8mg/kg (Max: 800mg/dose), one dose
Use at the discretion of Infectious Disease (ID) Physician and
intensivist for severe patients with evidence of cytokines release
syndrome (Supported by elevated inflammatory markers like CRP, d-
dimer, ferritin, etc)
Major side effects: hypertension, increased ALT, injection site infections,
risk of opportunistic infections particularly bacterial, anaemia; serious
side effects: gastrointestinal perforation, neutropenia
Live vaccines should be avoided for at least 3 months, after
commencement of tocilizumab.
6.10. Baricitinib
An orally administered, selective inhibitor of Janus Kinase (JAK) 1 and
2. Baricitinib inhibits the intracellular signaling pathway of cytokines
known to be elevated in severe COVID-19.
Among hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19 having elevated
inflammatory markers but not on invasive mechanical ventilation,
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 19 of 40
19)
concomitant use of baricitinib with remdesivir can be considered.
Baricitinib appears to demonstrate the most benefit in those with severe
COVID-19 on high flow oxygen or non-invasive ventilation at baseline.
The benefits for persons on mechanical ventilation are uncertain.
Dosing: oral 4mg once daily for up to 14 days of treatment or until
hospital discharge, whichever is first. Longer duration can be
considered at the discretion of ID physician/ ICU intensivist.
Renal adjustment: oral 2mg daily (30 to <60 ml/min), 1mg daily (15 to
<30 ml/min)
Use in combination with remdesivir. Limited information on the use of
baricitinib in combination with systemic corticosteroids. Consider use at
ID physician’s discretion
Potential side effects: Infection (particularly upper respiratory tract
infection, herpes zoster), nausea, raised ALT, neutropenia, arterial
thrombosis, malignant lymphoma (<1%), malignant neoplasm (<1%)
Not recommended for patients on dialysis, having eGFR <15ml/min,
having acute kidney injury, or having known active tuberculosis
Pregnancy: Should be used during pregnancy only if potential benefit
justifies the potential risk for the mother and the fetus
Avoid use of live vaccines with baricitinib
Monitoring: CBP, LRFT (Consider interruption if ALC <0.2 or ANC <0.5)
6.11. Casirivimab and imdevimab
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody products currently have
Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) from the Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-
19 patients who are at risk of progressing to severe disease and/or
hospitalization.
Casirivimab and imdevimab: These are recombinant human
monoclonal antibodies that bind to nonoverlapping epitopes of the
spike protein RBD of SARS-CoV-2.
Dosing: Casirivimab 600mg plus imdevimab 600mg intravenous
infusions for one dose. If intravenous route is not feasible,
administration by four subcutaneous injections (2.5ml per injection)
can be used as an alternative.
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 20 of 40
19)
The use of casirivimab and imdevimab can be considered in patients
with mild to moderate severity, at risk of progression to severe
COVID-19 infection and with a confirmed delta variant strain
Medical conditions or other factors that were represented in clinical
trials that evaluated anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies
•
Age >=65
•
Obesity (BMI >30)
•
Diabetes
•
Cardiovascular disease (including congenital heart disease) or
hypertension
•
Chronic lung disease (e.g. COPD, moderate to severe asthma,
interstitial lung disease, cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension)
Monoclonal antibodies should be used at discretion of ID physicians,
particularly for other conditions or factors at risk of progressing into
severe disease.
Side effects: Uncommon (up to 1 %): allergic reactions or reactions
following infusions: fever, chills, headache, difficulty breathing,
hypotension, facial swelling, itching, myalgia
Pregnancy: The safety for use in pregnancy is inadequate. Use if
potential benefits of treatment outweigh the potential risks to the
mother and fetus.
6.12. Monitoring during treatment
Blood x CBP, LRFT, LDH, CRP
Repeat DTS (or other respiratory specimens) x SARS-CoV-2 twice, 24
hours apart before isolation release
Repeat Stool x SARS-CoV-2 if there are previous positive results
before isolation release
Monitor for any concomitant bacterial or fungal infections
Observe for any side effects
7. Release from Isolation
Please refer to updated criteria for releasing confirmed COVID-19 patients from
isolation by CHP and HA
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 21 of 40
19)
8.
Follow-up arrangement
8.1.
Follow-up arrangement should be subject to parent team’s decision. In general,
patients who developed pneumonia or complications during hospitalization
should be monitored for any long term sequelae from COVID-19 infection
8.2.
Consider refer regional specialist clinic follow-up for patients who
are still symptomatic on discharge OR
had abnormal radiological changes for further review OR
had grossly abnormal biochemical parameters on date of discharge
8.3.
Subject to patient’s need, referral may be sent to clinical psychologist, medical
social worker, physiotherapist, occupational therapist, traditional Chinese
medicine practitioner or District Health Centre
8.4.
Monitoring during follow-up
Blood tests (e.g. CBP, LRFT, CRP) +/- 2 clotted blood for SARS-CoV2
antibody if not taken previously
CXR
Consider lung function tests for moderate to severe cases
Consider HRCT for cases with residual lung changes
# Individuals aged 18 years or above, including pregnant and breastfeeding women, are
recommended to receive three doses of COVID-19 vaccine (i.e. Comirnaty vaccine or
CoronaVac vaccine). (Source: Consensus Interim Recommendations on the Use of
COVID-19 Vaccines in Hong Kong (As of 6 April 2022). Available at
https://www.chp.gov.hk/files/pdf/consensus_interim_recommendations_on_the_use_of_
covid19_vaccines_in_hong_kong_6_apr.pdf
@ Medical conditions or treatments that may result in severe immunocompromise
include but are not limited to:
Active treatment for solid tumor and hematologic malignancies
Receipt of solid-organ transplant and taking immunosuppressive therapy
Receipt of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell or hematopoietic stem cell
transplant (within 2 years of transplantation or taking immunosuppression therapy)
Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency (e.g., DiGeorge syndrome, Wiskott-
Aldrich syndrome)
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 22 of 40
19)
Advanced or untreated HIV infection (people with HIV and CD4 cell counts
<200/mm3, history of an AIDS-defining illness without immune reconstitution, or
clinical manifestations of symptomatic HIV)
Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids (i.e., ≥20 mg prednisone or
equivalent per day when administered for ≥2 weeks), alkylating agents,
antimetabolites,
transplant-related
immunosuppressive
drugs,
cancer
chemotherapeutic agents classified as severely immunosuppressive, tumor-
necrosis (TNF) blockers, and other biologic agents that are immunosuppressive or
immunomodulatory
(e.g.,
B-cell
depleting
agents)
(Source:
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-
ncov/vaccines/recommendations/immuno.html (accessed 20/3/2022)
9. References
1. World Health Organization. Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-
nCoV) in suspected human cases. Interim guidance. 2020 Mar 19.
2. World Health Organization. Q&A on coronaviruses. 2020 Feb 2.
3. Hospital Authority. HA Communication Kit – Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-
19) Version 6.5. 2020 Dec 31.
4. Hospital Authority. Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of Cases of
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. 2020 Jan.
5. Centre for Health Protection, Department of Health. Factsheet on Coronavirus
Disease
2019
(COVID-19).
2020
Dec
31.
Available
at:
https://www.chp.gov.hk/en/healthtopics/content/24/102466.html
6. Centre for Health Protection, Department of Health. Communicable Disease
Surveillance Case Definitions Version 17.0. 2020 Apr 28.
7. Chan JF, et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel
coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster.
The lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395(10223):514-23.
8. Zhu N, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019.
New England journal of medicine. 2020 Jan 24.
9. Chu CM, et al. Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological
and clinical findings. Thorax. 2004 Mar 1;59(3):252-6.
10. Arabi YM, et al. Ribavirin and Interferon Therapy for Critically Ill Patients with
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome: A Multicenter Observational Study. Clin Infect
Dis. 2019 Jun 25.
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 23 of 40
19)
11. HKSARG. Press Release - SCEZD meeting held to review management of
COVID-19
patients.
2020
May
6.
Available
at:
https://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/202005/06/P2020050600679p.htm
12. To KK, et al. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva
samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an
observational cohort study. The Lancet infectious diseases. 2020 May
1;20(5):565-74.
13. Grein J, et al. Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19.
New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Jun 11;382(24):2327-36.
14. Wang Y, et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-
blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. The lancet. 2020 May
16;395(10236):1569-78.
15. Xu X, et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2020 May 19;117(20):10970-
5.
16. Cao B, et al. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-
19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Mar 18.
17. Hung IF, et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and
ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-
label, randomised, phase 2 trial. The Lancet. 2020 May 30;395(10238):1695-704.
18. Beigel JH, et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19—Final Report.
[published online October 8, 2020]. New England Journal of Medicine. doi.;10.
19. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with
Covid-19—preliminary report. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Jul 17.
20. Infectious Disease Society of America. Guidelines on the treatment and
management of patients with COVID-19. 2021 Jun 25.
21. WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19.
Interim WHO Solidarity trial results. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Dec
2.
22. Kalil AC, et al. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19.
New England Journal of Medicine. 2021 Mar 4;384(9):795-807.
23. World Health Organization. Living guidance for clinical management of COVID-
19. 2021 Jan 25.
24. National Institutes of Health. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment
Guidelines. Available at:
https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 24 of 40
19)
25. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with
COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial.
Lancet. 2021 May 1
26. Remap-Cap Investigators. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill
patients with Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2021 Apr
22;384(16):1491-502.
27. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Phase 3 Trial Shows REGEN‐COV™(Casirivimab
with Imdevimab) Antibody Cocktail Reduced Hospitalization or Death by 70% in
Non‐Hospitalized
COVID‐19
Patients.
2021.
Available
at:
https://investor.regeneron.com/news-releases/news-release-details/phase-3-
trial-shows-regen-covtmcasirivimab-imdevimab-antibody . Accessed 2021 Apr 5.
28. Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, et al. REGEN-COV antibody cocktail
clinical outcomes study in Covid-19 outpatients. MedRxiv. 2021 Jan 1. Available
at:
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.05.19.21257469v2
29. Jayk Bernal A, et al. Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized
patients. New England Journal of Medicine. 2022 Feb 10;386(6):509-20.
30. Merck & Co., Inc. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use
authorization
for
molnupiravir.
Available
at:
https://www.fda.gov/media/155054/download
31. Pfizer Inc. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for
Paxlovid. Available at:
https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download
32. UpToDate, Inc. Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir (United States and Canada: Authorized
for
use):
Drug
information.
Available
at:
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/lopinavir-and-ritonavir-drug-information/print .
Accessed 2022 Mar 7.
33. 无锡药明生物技术股份有限公司。安巴韦单抗注射液说明书。
34. 上海药明生物技术有限公司。罗米司韦单抗注射液说明书。
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 25 of 40
19)
Annex A. Important Drug Interactions with Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir)^
Paxlovid is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance
and for which elevated concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening
reactions:
• Alpha1-adrenoreceptor antagonist: alfuzosin
• Analgesics: pethidine, propoxyphene
• Antianginal: ranolazine
• Antiarrhythmic: amiodarone, dronedarone, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine
• Anti-gout: colchicine
• Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide, clozapine
• Ergot derivatives: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine
• HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: lovastatin, simvastatin
• PDE5 inhibitor: sildenafil (Revatio®) when used for pulmonary arterial hypertension
(PAH)
• Sedative/hypnotics: triazolam, oral midazolam
Paxlovid is contraindicated with drugs that are potent CYP3A inducers where significantly
reduced nirmatrelvir or ritonavir plasma concentrations may be associated with the
potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance. Paxlovid cannot be
started immediately after discontinuation of any of the following medications due to the
delayed offset of the recently discontinued CYP3A inducer:
• Anticancer drugs: apalutamide
• Anticonvulsant: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
• Antimycobacterials: rifampin
• Herbal products: St. John’s Wort (
hypericum perforatum)
^Please refer to Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers: Emergency Use Authorization for
Paxlovid (Table 1) for listing of clinically significant drug interactions (Available at:
https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download)
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 26 of 40
19)
Annex B. Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for
Severe COVID-19
1.
Higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes:
o
Cancer
o
Cerebrovascular disease
o
Chronic kidney disease*
o
Chronic lung diseases limited to:
Interstitial lung disease
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary hypertension
Bronchiectasis
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
o
Chronic liver diseases limited to:
Cirrhosis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease
Autoimmune hepatitis
o
Cystic fibrosis
o
Diabetes mellitus, type 1 and type 2*
o
Disabilities
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Cerebral Palsy
Congenital Malformations (Birth Defects)
Limitations with self-care or activities of daily living
Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
Learning Disabilities
Spinal Cord Injuries
o
Heart conditions (such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, or
cardiomyopathies)
o
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
o
Mental health disorders limited to:
Mood disorders, including depression
Schizophrenia spectrum disorders
o
Neurologic conditions limited to dementia
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 27 of 40
19)
o
Obesity (BMI ≥30 kg/m2)*
o
Primary Immunodeficiencies
o
Pregnancy and recent pregnancy
o
Physical inactivity
o
Smoking, current and former
o
Solid organ or hematopoietic cell transplantation
o
Tuberculosis
o
Use of corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications
2.
Suggestive higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes:
o
Children with certain underlying conditions
o
Overweight (BMI ≥25 kg/m2, but <30 kg/m2)
o
Sickle cell disease
o
Substance use disorders
o
Thalassemia
3.
Mixed evidence:
o
Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
o
Asthma
o
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
o
Hepatitis B
o
Hepatitis C
o
Hypertension*
Footnote: * indicates underlying conditions for which there is evidence for pregnant and
non-pregnant people
(Source: Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for Severe COVID-
19: Information for Healthcare Professionals. US CDC. Updated Feb. 15, 2022.
Available at
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html)

 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 28 of 40
19)
Annex C. Information and Consent form for experimental treatment of COVID-19
Information and Consent form
for experimental treatment of COVID-19
(14 April 2022 version)
Up till now, there is no consensus on international recommendation of using specific
antiviral agents for treatment of COVID-19. However, there have been evidences
(including in vitro studies, animal models, case studies, observational studies, as well as
some randomized controlled trials (RCT) suggesting possible clinical benefits for the
following agents:
Interferon β-1b (subcutaneous injection)
Casirivimab and imdevimab (intravenous or subcutaneous injection)
Amubarvimab/romlusevimab (intravenous infusion)
Interferon β-1b is registered medication in Hong Kong. It has been used to manage
multiple sclerosis. The unlicensed use of this drug to treat COVID-19 is experimental,
not standard treatment. Casirivimab and imdevimab, mubarvimab/romlusevimab are
unregistered drugs in Hong Kong.
The above listed drugs have potential side effects (see table below), but their side effects
will be closely monitored. If the risk of the drugs is considered to outweigh their benefits,
the drugs will be stopped immediately. Moreover, the treatment regimen is subject to
change according to the latest evidence from studies and updates in overseas guidelines.
For enquiries, please contact our health care staff for assistance.
Potential side effects of the drugs listed below include but not limited :
Interferon β-1b
Flu-like symptom complex (fever, chills, arthralgia,
malaise,
sweating,
headache,
or
myalgia),
neutropenia, decreased blood glucose, depression,
anxiety, headache, dizziness, insomnia, etc.
Casirivimab and imdevimab
Allergic reactions or reactions following infusions:
fever, chills, headache, difficulty breathing,
hypotension, facial swelling, itching, myalgia
Amubarvimab/romlusevimab Allergic reactions, hypersensitivity reactions,
infusion-related
reactions
including
pyrexia,
dyspnea, desaturation, chills, fatigue, arrhythmia,
chest pain, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, change in
mental status, nausea, headache, bronchospasm,
hypotension, hypertension, vasogenic edema, rash,
pruritus, myalgia, vasovagal reactions, dizziness,
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 29 of 40
19)
profuse sweating; possible COVID-19 clinical
deterioration; No available human data on the use of
this drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding; If you
have any question and for details, please refer to
drug product insert and consult your attending
doctor.
Consent
I understand the limitations and potential side effects of the above medications under
the condition of unlicensed use, and I do freely give my consent to accept the treatment
below:
□ Interferon β-1b
□ (Female) Pregnancy test negative
□ (Female) Pregnancy test positive. Explained benefits and potential risks in details
□ Casirivimab and imdevimab
□ Amubarvimab/romlusevimab
□ Other treatment _____________________
Patient's signature ___________________________ Date __________________________
Patient’s name ______________________________
Witness’s signature __________________________ Date __________________________
Witness’s name _____________________________
Doctor’s signature ___________________________ Date __________________________
Doctor’s name ______________________________

 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 30 of 40
19)
關於
2019 年新型冠狀病毒感染
(
COVID-19)
試驗性質藥物治療的資料及同意書
(
2022 年
04 月
14 日版本)
迄今為止,尚未有國際準則關於抗病毒藥物在新型冠狀病毒感染(
COVID-19)有明確的臨床效果。但根據
其他有限證據(包括體外研究、動物模型、案例研究、內地及本地專家的意見、一些隨機對照試驗(Randomized
controlled trial)),病者可以考慮接受以下藥物治療。
干擾素β-1b(interferonβ-1b)(皮下注射)
抗體療法 (casirivimab and imdevimab)(靜脈或皮下注射)
安巴韋單抗/羅米司韋單抗單抗(amubarvimab / romlusevimab)(靜脈注射)
干擾素β-1b 是在香港註冊的藥物,用於治療多發性硬化症。但在未經許可情況下使用藥物(unlicensed use)
治療 2019 年新型冠狀病毒感染(COVID-19)屬於試驗性質,並不是對 COVID-19 的標準治療。抗體療法
(casirivimab and imdevimab)和安巴韋單抗/羅米司韋單抗單抗(amubarvimab / romlusevimab)在香港是未
經註冊的藥物。
以上藥物有機會出現潛在副作用(見下表)
,但藥物的副作用將受到密切監測,如果發現風險大於益處,醫
生會即時終止治療。另外,治療方案亦可能隨着最新的研究數據和各地指引的更新而有所調整,希望能令病
者得到最理想的治療效果。
如有查詢,請聯絡我們的醫護人員尋求協助。
以下藥物的潛在副作用包括但不限於:
干擾素 β-1b
流感樣症狀 (發燒,發冷,關節痛,出汗,頭痛或肌痛)
,注射部位反應 (發
紅,腫脹,變色,發炎,疼痛)
,白細胞下降,血糖下降,抑鬱,焦慮,頭痛,
頭暈,失眠等等
抗體療法
過敏反應,注射部位反應, 發燒,發冷,頭痛,呼吸困難,低血壓,面部腫脹,
發癢,肌痛
安 巴 韋 單 抗 / 羅 米 司 韋
過敏反應、超敏反應、輸液相關反應包括發熱、呼吸困難、去飽和、寒顫、疲
勞、心律失常、胸痛、精神狀態改變、噁心、頭痛、支氣管痙攣、低血壓、高
單抗
血壓、血管源性水腫、皮疹、瘙癢、肌痛、血管迷走神經反應、頭暈、大量出
汗; COVID-19 臨床病情惡化;至目前為止,沒有數據關於人類在懷孕期間使用
安巴韋單抗/羅米司韋單抗,會否導致胚胎或胎兒受損或出現缺陷、流產或母體
受損或不良反應。至目前為止,沒有數據關於人類或動物母乳中存在或排泄安
巴韋單抗/羅米司韋單抗。如有任何問題,詳情請參閱藥品說明書並諮詢您的主
治醫生
同意書
本人明白在未經許可的情況下使用以下藥物(unlicensed use)的局限性及潛在的副作用,並同意接受以下治
療。
□ 干擾素β-1b (interferonβ-1b)
□ (女性)驗孕結果陰性
□ (女性)驗孕結果陽性 : 使用藥物前已經向病人詳細解釋干擾素 β-1b 的益處、潛在風險和副作用
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 31 of 40
19)
□ 抗體療法(casirivimab and imdevimab)
□ 安巴韋單抗/羅米司韋單抗單抗(amubarvimab + romlusevimab)
□ 其他: _________________
病人簽署 ___________________________
日期 __________________________
病人姓名 ____________________________
見證人簽署 __________________________
日期 __________________________
見證人姓名 __________________________
醫生簽署 ____________________________
日期 __________________________
醫生姓名 ____________________________
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 32 of 40
19)
Annex D. Fact sheet on the use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (PaxlovidTM)
Use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in COVID-19 patients
(Version 1, 21 March 2022)
PaxlovidTM is nirmatrelvir tablets co-packaged with ritonavir tablets. Nirmatrelvir is a
SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitor, and ritonavir is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor
and CYP3A inhibitor. The product is conditionally approved with limited safety, efficacy,
and quality data for public health emergency to satisfy local unmet medical need in Hong
Kong.
Contraindications
Patients less than 12 years of age or weighing below 40kg
History of clinically significant hypersensitivity reactions to the ingredients or
components of the product
Warnings and precautions
Hepatotoxicity: Hepatic transaminase elevations, clinical hepatitis, and jaundice
Risk of developing drug resistance to HIV protease inhibitors in individuals with
uncontrolled or undiagnosed HIV-1 infection
Examples of significant/potentially significant drug interactions [consult full
prescribing information if needed]
•
Alpha1-adrenoreceptor antagonist: alfuzosin
•
Analgesics: pethidine, propoxyphene
•
Antiarrhythmic: amiodarone, dronedarone, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine
•
Antimycobacterial: rifampicin
•
Anticancer drug: apalutamide
•
Anticoagulants: warfarin, rivaroxaban
•
Anticonvulsant: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
•
Anti-gout: colchicine
•
Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide, clozapine
•
Cardiac glycosides: digoxin
•
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: atorvastatin, lovastatin, rosuvastatin,
simvastatin
•
Hormonal contraceptive: ethinyl estradiol
•
PDE5 inhibitor: sildenafil when used for pulmonary arterial hypertension
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 33 of 40
19)
•
Sedative/hypnotics: triazolam, oral midazolam
Adverse reactions Dysgeusia (altered sense of taste), diarrhoea, hypertension (high blood pressure),
myalgia (muscle aches)
Dosage and administration
300 mg nirmatrelvir (two 150 mg tablets) with 100 mg ritonavir (one 100 mg tablet)
taken orally every 12 hours for 5 days, with or without food
Moderate renal impairment
(eGFR ≥30 to <60 mL/min): 150 mg nirmatrelvir
(one 150 mg tablet) with 100 mg ritonavir (one 100 mg tablet) taken orally every
12 hours for 5 days, with or without food
Severe renal impairment
(eGFR <30 mL/min): NOT recommended
Severe hepatic impairment
(Child-Pugh Class C): NOT recommended
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 34 of 40
19)
新冠肺炎口服抗病毒治療藥物
奈瑪特韋
(nirmatrelvir) / 利托那韋
(ritonavir)須知
(第
1 版,
2022 年
3 月
21 日)
帕 克 斯 洛 維 德 (PaxlovidTM) 包 裝 內 含 有 兩 種 藥 物 , 奈 瑪 特 韋 (nirmatrelvir) 和 利 托 那 韋
(ritonavir)。Nirmatrelvir是一種SARS-CoV-2主要蛋白酶(Mpro)的擬肽抑制劑,而ritonavir是
一種 HIV-1 蛋白酶抑制劑。雖然只有有限的安全性、效能及素質的資料,在公共衞生緊
急事態以及本地的醫療需要下,帕克斯洛維德在本港已獲得有條件批准註冊。
以下人士不可使用帕克斯洛維德
(PaxlovidTM)
12 歲以下或體重少於 40 公斤的病人
曾對帕克斯洛維德中的任何成分有嚴重過敏史
警告和注意事項
肝臟毒性 : 出現肝轉氨酶升高、臨床肝炎和黃疸
對 HIV 藥物的抗藥性 : 在未受控制或未經治療的 HIV 感染情況下,帕克斯洛維德
可能會影響某些 HIV 藥物在未來發揮作用
以下藥物相互作用例子可能會導致嚴重副作用或影響帕克斯洛維德的藥效(如有需要,
請查閱詳細藥物資料)
•
α1 -腎上腺素能受體拮抗劑:alfuzosin
•
止痛藥:pethidine, propoxyphene
•
抗心律不正藥:amiodarone, dronedarone, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine
•
抗結核病藥:rifampicin
•
抗癌藥物:apalutamide
•
抗凝血藥:warfarin, rivaroxaban
•
抗腦癇藥:carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
•
抗痛風藥:colchicine
•
抗精神病藥:lurasidone, pimozide, clozapine
•
洋地黃類藥:digoxin
•
HMG-CoA 還原酶抑制劑 (他汀類):atorvastatin, lovastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin
•
荷爾蒙避孕藥 : ethinyl estradiol
•
PDE5 抑制劑:sildenafil (用於治療肺動脈高壓)
•
鎮靜/安眠藥:triazolam, oral midazolam
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 35 of 40
19)
副作用
味覺改變、腹瀉、高血壓、肌肉疼痛
劑量
每 12 小時一次,每次 300 毫克 nirmatrelvir (兩粒 150 毫克藥丸)
和 100 毫克 ritonavir
(一粒 100 毫克藥丸),空肚或飽肚服用均可,整個療程為期五天。
中度腎功能不全病人(eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min): 每 12 小時一次,每次 150 毫克
nirmatrelvir (一粒 150 毫克藥丸)
和 100 毫克 ritonavir (一粒 100 毫克藥丸),空肚
或飽肚服用均可,整個療程為期五天。
嚴重腎功能不全病人(eGFR <30 mL/min): 不建議使用
嚴重肝功能不全病人(Child-Pugh Class C): 不建議使用
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 36 of 40
19)
Annex E. Fact sheet on the use of molnupiravir
Use of molnupiravir in COVID-19 patients
(Version 2, 21 March 2022)
Molnupiravir is a nucleoside analogue that inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication by viral
mutagenesis. The United States Food and Drug Administration has granted emergency
use authorization (EUA) to molnupiravir.
Contraindications
Pregnancy
Breastfeeding
Patients less than 18 years of age
Warnings and precautions:
Embryo-fetal toxicity
Allergic reactions: stop if it occurs.
Bone and cartilage toxicity: molnupiravir should not be used in patients less than 18
years of age because it may affect bone and cartilage growth.
Adverse reactions
Diarrhea, dizziness, headache, skin itchiness, skin rash, nausea, vomiting.
Laboratory abnormalities in kidney and liver functions tests and haematology
(haemoglobin, platelets, and leukocytes)
Dosage and administration: 800 mg (four 200 mg capsules) taken orally every 12 hours
for 5 days, with or without food.
Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment.
Hepatic impairment: No dosage adjustment.
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 37 of 40
19)
醫院管理局
新冠肺炎口服抗病毒治療藥物莫納皮拉韋(
Molnupiravir)須知
(第
2 版,
2022 年
3 月
21 日)
莫納皮拉韋(Molnupiravir)是一種有醫學實證能夠治療新冠肺炎的口服抗病毒藥物,用於
輕度及中度病情有高風險未接種疫苗的新冠肺炎患者,能有效減低入院率及死亡率。莫納
皮拉韋已獲得美國食品和藥物管理局授權緊急使用(EUA),但在香港並未註冊。如要在
香港臨床上使用,必須先徵求病人或家屬的同意。
以下人士不可使用莫納皮拉韋
懷孕女性(莫納皮拉韋對胚胎或胎兒有害)
哺乳女性(莫納皮拉韋對胚胎或胎兒有害)
十八歲以下人士(莫納皮拉韋可能會影響骨和軟骨的生長)
警告和注意事項
莫納皮拉韋治療對胚胎及胎兒毒性
建議有生育能力的女性,在莫納皮拉韋治療期間,和在服用最後一劑莫納皮拉韋
後的 4 天內,正確和一致地使用有效的避孕方法
建議有生育能力的男性,在莫納皮拉韋治療期間,和在服用最後一劑莫納皮拉韋
後的 3 個月內,正確和一致地使用有效的避孕方法(註:直到目前為止,醫學界
尚未清楚男性在服用最後一劑莫納皮拉韋 3 個月後,莫納皮拉韋會否對他們的子
女產生胚胎或胎兒異常、傷害或毒性風險)
過敏、嚴重過敏反應、血管性水腫、紅斑、皮疹和蕁麻疹、化學(ALT、AST、肌酐
和脂肪酶)和血液學(血紅蛋白、血小板和白細胞)的化驗報告異常等
副作用
在醫學臨床研究中其副作用與安慰劑相約
較為可預見(<2%)的副作用包括:過敏反應、頭暈、嘔心、腹瀉等
 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 38 of 40
19)
劑量
每 12 小時一次,每次 800 毫克(四粒膠囊),一個療程為期五天

 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 39 of 40
19)
Annex F. Quick sheet on oral antiviral for COVID-19 treatment

 HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases
HA Central Committee on Infectious Diseases Ref No.
CCIDER-COVID19-001(v1.12)
and Emergency Response (CCIDER)
Issue Date
14 April 2022
Review Date
13 February 2023
Interim Recommendation on Clinical Management of
Approved by
CCIDER
Adult Cases with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-
Page
Page 40 of 40
19)
Annex G. Principles of prescription of Paxlovid (oral antiviral) for treatment of early COVID-19 infection











































